What is LEMS?
Important facts about Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)
LEMS IS a rare neuromuscular disorder (a condition that affects the nerves and muscles) that typically causes severe, debilitating, and progressive muscle weakness and fatigue.
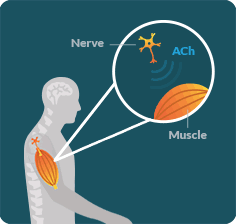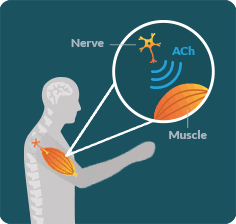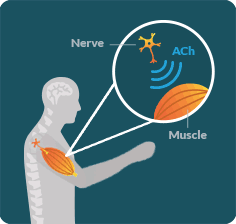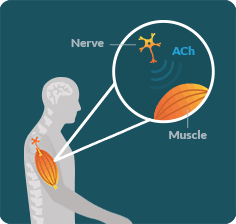
LEMS OCCURS WHEN a specific antibody disrupts the communication between the nerves and muscles in an area known as the neuromuscular junction (NMJ).
IN LEMS, special proteins called antibodies impact certain calcium channels along the neuron, resulting in decreased secretion of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (ACh). Without enough ACh, signals cannot be transmitted between the nerves and muscles. This disruption keeps the muscles from working properly.
WHO IS AFFECTED BY LEMS?
SYMPTOMS OF LEMS include muscle weakness, especially in the legs and hips. This weakness may fluctuate from day to day. LEMS can make it very difficult to do everyday activities, such as walking, talking, or lifting objects. Some patients may have to use assistive equipment, such as a wheelchair or walker, to get around. If you suspect that you may have LEMS, talk to your doctor about the symptoms you’re experiencing and your possible treatment options.
LEMS IS OFTEN MISDIAGNOSED AS SOME OTHER CONDITION INITIALLY
More than 1/3 of diagnosed LEMS patients were previously diagnosed as having myasthenia gravis (MG).
Many people with LEMS struggle with symptoms for years before finally getting diagnosed. For that reason, it’s important to see a physician who has experience with diagnosing neuromuscular diseases.
Who treats LEMS?
If you think that you may be experiencing symptoms of LEMS, talk to your physician. If your physician suspects that you may have LEMS, he or she may refer you to a neurologist or neuromuscular specialist. These types of doctors specialize in neuromuscular diseases like LEMS. Find a LEMS physician nearest to you now.
How LEMS is diagnosed
LEMS may be diagnosed by a physical exam and confirmed by one or both of the following:
Benefits of earlier diagnosis
An early, accurate diagnosis may help you in several ways:
MORE ABOUT LEMS AND CANCER
For some patients, their LEMS symptoms are an important early warning sign that may help save their lives. The timing of LEMS is variable: LEMS symptoms, including muscle weakness, can appear ≥ 5 years before, after, or at the time of cancer diagnosis—and those symptoms can worsen at any time.
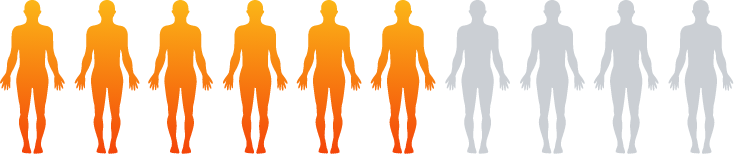
Approximately 50% to 60% of people with LEMS also have, or will have,
a co-occurring cancer—often small cell lung cancer
Your treating physician may recommend cancer screenings when you are diagnosed with LEMS and periodically thereafter.